|
Extremely thin printable solar panels could power your phone and are amongst a range of new ways nanotechnology is opening the door to a clean energy and waste-free future.
PHYS.ORG — Nanotechnology, a science that focuses on understanding materials on an atomic scale, is helping researchers and businesses introduce new technologies that could transform our economy into a greener, less wasteful one. "Nanotechnology as a field has an enormous role to play in moving our planet to sustainable and intelligent living," said Professor Martin Curley from Maynooth University in Ireland, speaking on 21 June at the EuroNanoForum conference. He explained to an audience of businesspeople and researchers that nanotechnology holds the potential to spark 'an explosion of innovation". One area where this innovation could have its biggest impact is with how we generate, use and consume energy. Speaking at a session dedicated to nanotechnology in clean energy generation, Prof. Alejandro Pérez-Rodríguez, from the department of electronics at the University of Barcelona, said solar energy and photovoltaic technology itself could be considered a nanotechnology sector. "In all PV technologies and devices we put some nanotechnology … If we want to move to devices with higher functionality, lower weight, higher flexibility, different colors, then we need to integrate more nanotechnologies into their materials and architecture." At the same session, Artur Kupczunas, co-founder of Saule Technologies, explained how his company is using nanotechnology to print solar panels using perovskite crystals, a cheap and highly sensitive mineral that was first found in the Ural Mountains of Russia in 1839. They produce thin layers of solar cells that are somewhere near one-tenth of the thickness of a single human hair. This innovation could greatly reduce the cost of producing solar energy while transforming any surface into a solar panel, from walls and roadside barriers to the surface of your smartphone. "The most interesting factor is the (reduction of) overall costs," said Kupczunas, explaining that this means the technology could be easily scaled out across the market. Fuel cell At the same session, John Bøgild Hansen, a senior scientist from Haldor Topsøe, a Danish chemical engineering company, explained how they have been using nanotechnology to look at the atomic level of gases in order to better understand their properties. This knowledge contributed to creating a fuel cell for greener biofuel production. Their process extracts pure hydrogen from plant materials while reusing any CO2 emissions created during the process to help power the production cycle, preventing any fossil fuels entering the atmosphere. This, he believes, is a way to 'break the bottleneck' on biofuels which currently struggle to get public and private support. "If we want the conveniences we have today from liquid energy carriers (oil, natural gas etc.) for transport … hydrocarbons (biogas) are the best," he said. Storing wind and solar energy during unstable weather is another gap in our sustainable energy future. Professor Magnus Bergen and his team at Sweden's Linköping University are looking into using nanotechnology to harness the molecular properties of a plastic conductive material called PEDOT:PSS. They combine this knowledge with nanocellulose, a product made from plants or oil, to create an organic material that stores energy. "If we make a (PEDOT:PSS) battery the size of a refrigerator it can store (enough energy for) the needs of a family in a house or an apartment for a day," he said. Because of its ability to charge quickly, it could be a way to compensate for the under- or over- production of wind and solar energy during calm or cloudy days. This, in turn, could break cities' dependency on fossil fuels. "You need to store when you are over-producing and release when you are under-producing," Prof. Bergen explained. Waste-free Nanotechnology also has the ability to make technology smaller, extend the life-cycle of electronics, improve manufacturing processes, all of which would mean less waste has to go to the landfill. Speaking at one of the sessions, Joe Murphy, from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, an association in the UK dedicated to promoting waste as a resource, explained nanotechnologies 'may enable us to create a new material palette' that allows future products to be recycled more easily. "At the moment we have a lot of barriers to recycling … nanotechnology may enable us to do more," he said.
1 Comment
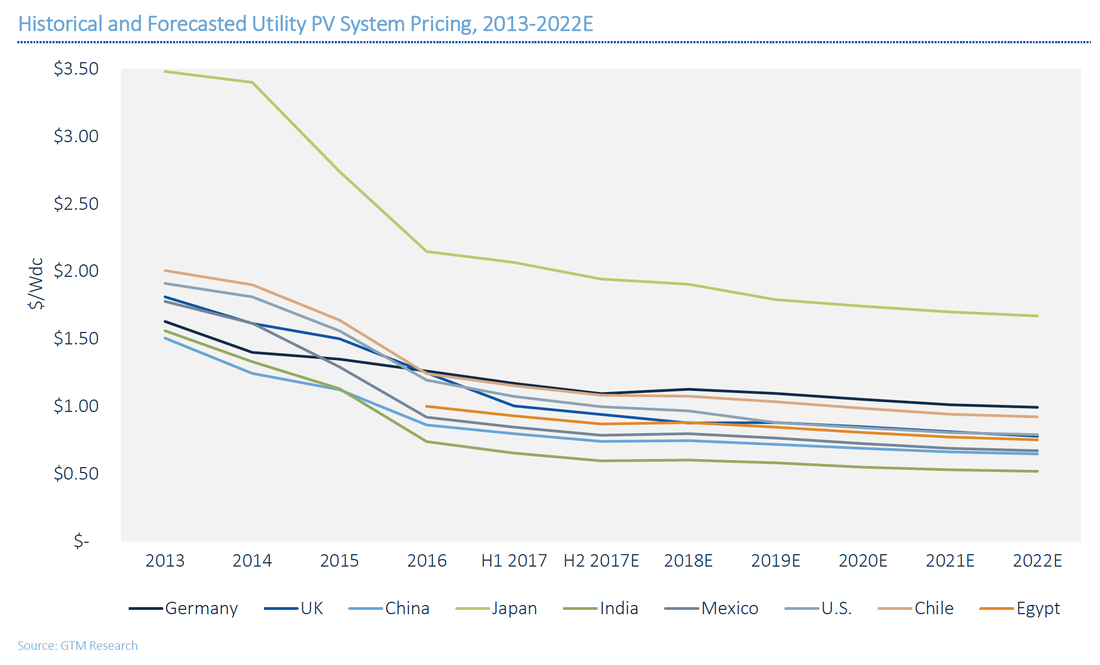
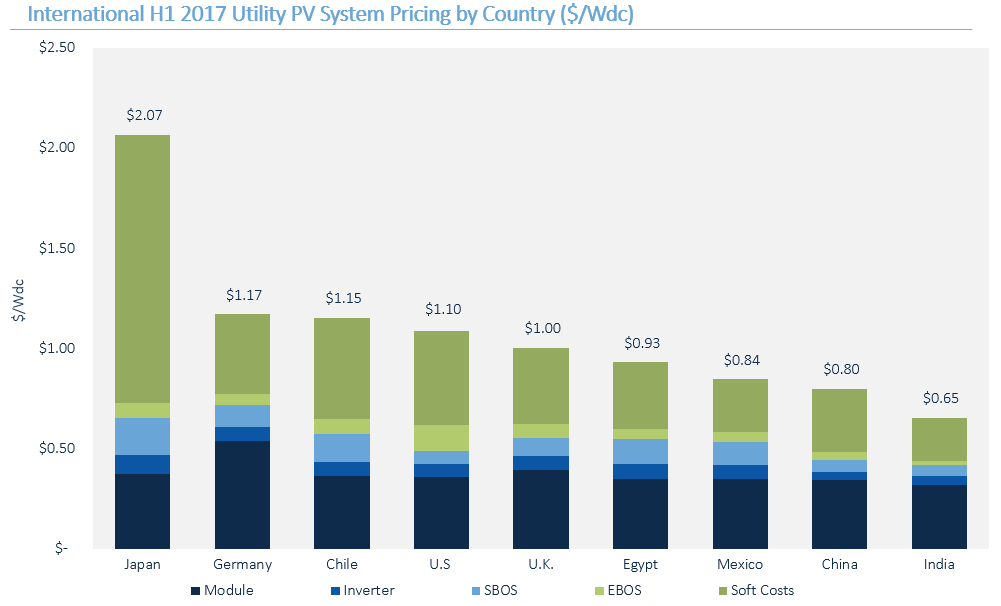
SOLAR COSTS ARE HITTING JAW-DROPPING LOWS IN EVERY REGION OF THE WORLD How low can you go? Mind-blowingly low 65-cents-per-watt solar system pricing emerges in India. GREENTECH MEDIA — This may sound a little repetitive since this has been a repeating narrative, but now it's impossible to ignore: The decline in solar costs is not slowing down. GTM Research expects a 27 percent drop in average global project prices by 2022, or about 4.4 percent each year. Those improvements are not limited to the U.S. They are occurring globally, and in some cases resulting in even sharper price declines than those America is experiencing. The data comes from a new PV system pricing forecast from GTM Research Solar Analyst Ben Gallagher. The plunges in system pricing won't just come from modules -- they'll come from reductions in inverters, trackers and even labor costs. And every region will benefit. "Component prices are beginning to lose their price variance from country to country," writes Gallagher. "Beyond a handful of local content requirements, many of the policies that created regional hardware pricing have been eroded by market forces." In the U.S., it's only stubborn soft costs such as customer acquisition that have actually risen And it's seemingly only trade disputes that can derail the price-decrease train. 65 cents per watt? GTM Research finds that India’s system of tenders has produced extremely competitive bidding, and, as a result, almost unimaginably low system pricing. India is seeing the lowest system prices of any major solar market in the world, ever. The report finds that India has utility PV system pricing of 65 cents per watt. The secret to these low prices? It turns out that a great way to reduce your soft costs is to pay your labor force and engineers next to nothing. (Markets with low-cost labor are more likely to use fixed-tilt systems, lowering turnkey system prices even more.) As the report points out, even in China soft costs are 11 cents per watt higher than in India. The compression in India's soft costs is well illustrated in the following chart Is that sustainable? Or even a positive thing? The reports points out the negatives of low pricing.
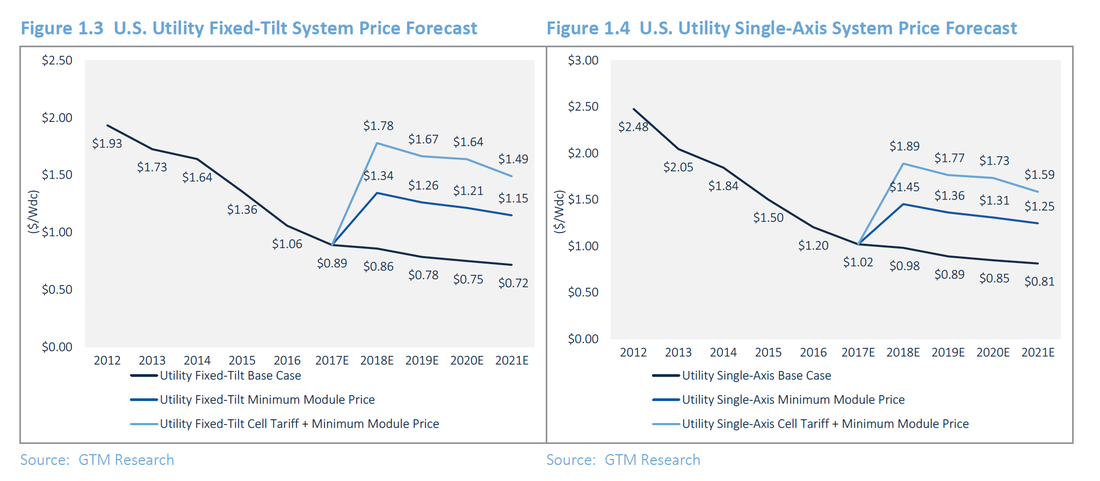
"The competitive tender process has a harmful side effect: There are reportedly widespread concerns about the viable lifetimes of many of the systems currently installed, as it is suspected that many were hastily constructed using poor-quality components. Developers will look to [engineering, procurement and construction providers] to safeguard their investment by raising installation and procurement quality-control standards and reduce long-term O&M headaches," writes Gallagher. The report also takes a close look at price trends in China, Mexico, India, Germany and the U.K. Japan is the highest-priced market, with systems landing at $2.07 per watt, driven by heavy wind, earthquakes and mountainside erosion that add additional engineering scrutiny and costs. The U.K. has the lowest-priced solar in Western Europe, largely because of common adoption of string inverters, which shaves a few pennies per watt. America's new trade case is a crapshoot The Section 201 trade complaint from Suniva and SolarWorld hangs like the sword of Damocles over the solar industry's head. Pricing for multicrystalline modules fell by 12 percent from H2 2016 to H1 2017. But in H2 2017, module pricing will increase: The U.S. market will see pull-in as buyers look to build up inventory before the final ruling. Although the result of the case won't be known until much later in the year, the filing suggests a possible penalty on all imported silicon PV modules of $0.78 per watt -- $0.41 cents higher than current U.S. module pricing. Suniva advises that the floor price step down to $0.72, $0.69 and $0.68 per watt in years two, three and four, respectively. It is also asking for a minimum price of $0.40 per watt on imported cells. GTM Research also just released a brand-new analysis on the potential impact to demand. According to Cory Honeyman, the associate director of GTM's solar practice, those penalties could result in the destruction of tens of gigawatts of solar installations in the U.S. through 2022. "In our latest report, we found that between 2018 and 2022, total U.S. solar installations would fall from 72.5 gigawatts cumulatively to just 36.4 gigawatts under a $0.78 per watt minimum module price scenario," writes Honeyman. Here's how pricing for utility-scale solar would be impacted: Philadelphia announced today that it has committed to transitioning to 100 percent clean energy.
CURBED — “In Philadelphia we’re not afraid of hard work and will do everything in our power to fight climate change,” Philadelphia Mayor Jim Kenney said. The city’s commitment to 100 percent clean and renewable energy makes Philadelphia the 100th city—and the second largest city, at that—to sign onto the Mayors for 100% Clean Energy effort spearheaded by the Sierra Club. Local universities and college institutions, including Drexel University, have also signed the We Are Still In pledge to meet the goals of the Paris climate agreement. The Sierra Club’s overall target year for cities to transition to 100 percent renewable energy is 2035. Sara Wu, deputy director of the Office of Sustainability, clarified that the 2035 date is just a goal: “While we’re being aspirational and setting the goal of 100 percent clean energy, we’re still working to understand what it would take to meet that goal within a specific timeframe.” Nearly 300 mayors of U.S. cities have adopted the Paris climate accord after the U.S. pulled out of the agreement, which is a non-binding contract that encourages countries to lessen their carbon footprint in an attempt to fight the global effects of climate change. Philadelphia’s renewed efforts come after Kenney stated on June 1 that the city would be updating guidelines already in place for the city for its residents to take action against climate change. Managing director Mike DiBerardinis pointed to the city’s current city efforts, which include an ongoing master energy plan and the mayor’s Zero Waste initiative to prevent waste and reduce litter by 2035. Most recently, SEPTA announced that it would be installing the second largest solar panel system in the city at four of its stations. There are also plans in place to reduce emissions from all city vehicles, DiBerardinis added. The city’s utilities are already purchasing renewable energy, with a focus on increasing efficiency and reducing the amount of energy used, said Christine Knapp, director of Philadelphia’s Office of Sustainability. In April, City Council passed a moratorium on the bill, which previously allowed electric car owners to install car-charging stations by their homes. Knapp acknowledged by the moratorium “might be upsetting” to some, but assured that the goal is to revamp the way the bill works so that it’s “way more accessible.” Less than 60 parking permits had been issued since the original bill passed 10 years ago. Now that the cost of electric cars is coming down, Knapp said, “the ultimate outcome is going to allow a lot more people to take advantage. It’s sort of a slight pause with progress to come.” Kenney also announced that the city has made available online all of the climate data that was recently scrubbed from the Environmental Protection Agency website in April. This information, which includes background on why and how climate is changing, is now available at https://beta.phila.gov/climatechangeisreal, with open-source code available so other cities can copy the site to their own respective sites. Leaders from more than 250 cities unanimously back a resolution to reach clean energy goal at the US Conference of Mayors in Miami Beach.
THE GUARDIAN — A bipartisan group of mayors from across the country has unanimously backed an ambitious commitment for US cities to run entirely on renewable sources such as wind and solar by 2035. As the US Conference of Mayors wrapped up in Miami Beach on Monday, leaders from more than 250 cities voted on symbolic resolutions pushing back against Donald Trump on climate change and immigration. Steve Benjamin, the Democratic mayor of Columbia, South Carolina, proposed the resolution with three other mayors. Mayors had been on the frontline of climate and energy issues for a long time, he said, adding that the president’s actions had ignited the excitement of mayors and citizens who want to do more. The clean energy resolution is one of the many measures that will be sent to Congress and the White House, hoping to influence legislation under an administration that has pulled the US out of the Paris climate accord. It was proposed by Democratic mayors in Republican-dominated states: South Carolina, Texas, Utah and Iowa. Miami Beach mayor Philip Levine was another leader of the effort after being in the spotlight for his moves to combat sea level rise. A May survey by the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions said 47 cities spent nearly $1.2bn annually on electricity for city operations. Mayors at the conference have overwhelmingly expressed support to fight climate change, especially after the Trump administration pulled out of the Paris climate agreement last month. “I think most mayors in America don’t think we have to wait for a president” whose beliefs on climate change are disconnected from science, New Orleans mayor and new conference president Mitch Landrieu said at the beginning of the conference. “There’s near unanimity in this conference that climate change is real and that humans contribute to it. There may be a little bit of a disagreement about how actually to deal with it. “If the federal government refuses to act or is just paralyzed, the cities themselves, through their mayors, are going to create a new national policy by the accumulation of our individual efforts.” CALIFORNIA IS EMBARRASSING THE REST OF THE COUNTRY WITH THE AMOUNT OF SOLAR ENERGY IT'S PRODUCING6/26/2017 California is the poster child for solar energy: in 2016, 13% of the state's power came from solar sources.
BUSINESS INSIDER — According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, California is in the lead for the cumulative amount of solar electric capacity installed in 2016. In fact, the California is generating so much solar energy that it is resorting to paying other states to take the excess electricity in order to prevent overloading power lines. According to the Los Angeles Times, Arizona residents have already saved millions in 2017 thanks to California’s contribution. The state, which produced little to no solar energy just 15 years ago, has made strides — it single-handedly has nearly half of the country’s solar electricity generating capacity. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, California reached a milestone: for a few hours, more than half the state's power needs were sourced from solar energy. This put wholesale energy prices in the negative. When there's too much solar energy, there is a risk of the electricity grid overloading. This can result in blackouts. In times like this, California offers other states a financial incentive to take their power. But it’s not as environmentally friendly as one would think. Take Arizona, for example. The state opts to put a pin in its own solar energy sources instead of fossil fuel power, which means greenhouse gas emissions aren’t getting any better due to California’s overproduction. California’s state goal is to get 50% of all its electricity from renewable sources by 2030. Faced with pollution and rising sea levels, cities are setting targets at a record pace.
GREENTECH MEDIA — Cities are increasingly moving ahead of countries in setting carbon-reduction goals and initiatives, according to a new report from banking giant HSBC. More than 2,500 cities have now listed climate-change pledges on the Non-State Actor Zone for Climate Action (NAZCA) portal launched as part of the 2014 Lima-Paris Action Agenda, HSBC notes. “We think this is extremely important because NSAs [non-state actors] can move quicker in implementing climate change policies and measures,” reads the report. Cities and other NSAs tend to be faster than countries at making decisions, and are more accountable to their local electorates. They may also have greater control over which budgets can be assigned to climate-change mitigation policies. Some experts, however, warn that cities are having serious problems implementing their own climate goals. Metropolitan centers have much to lose from inaction. Cities account for up to 70 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions, and many are already experiencing major levels of pollution. This causes 3 million deaths a year, according to the World Health Organization. Dangerous levels of airborne particulate matter are a common feature of emerging market cities such as Gwalior or Allahabad in India, or Riyadh in Saudi Arabia. But they are also found in major financial centers such as Paris, London or Stuttgart. Dealing with air pollution is a pressing problem, but one that may pale compared to the looming risks associated with global warming. With many major cities in coastal areas, 71 percent of the world’s population might be exposed to rising sea levels by 2025. In Latin America, the proportion of the population living in low-elevation coastal zones could be as high as 90 percent. City populations will also be more prone to higher urban temperatures, vector-borne diseases and allergen levels, HSBC predicts. Health aside, the investment bank cites OECD data showing that by 2070 up to $35 trillion in assets could be at risk from coastal flooding in large cities. Given the magnitude of these threats, it is not surprising that many cities have opted to take climate-change mitigation measures into their own hands. The Paris Agreement prompted a 70 percent increase in the number of cities disclosing climate data, with urban centers such as Copenhagen, Melbourne and Stockholm announcing plans to become completely carbon neutral. “In the U.S., where President Trump has signed an executive order to pull out of the Paris Agreement, it is encouraging from a climate standpoint that 93 cities have pledged commitments to climate action through the NAZCA portal,” reads the report. It lists 28 countries that now have 10 or more "climate-smart cities" with city-level climate pledges. Europe leads the trend, with 646 cities lining up to cut emissions in Italy alone. Elsewhere, there are significant climate-smart city movements in nations from Mexico to Japan. One country that stands out, HSBC says, is Canada. There, 21 cities have made climate pledges. Canada’s 10 largest cities account for around half of the country’s population and are on a path to achieve a 40 percent emissions reduction by 2030, on average. This would achieve 17.2 percent of Canada’s national target of a 30 reduction by 2030, according to HSBC. Jonathan Walters, a former World Bank director who now works as an independent economic consultant on energy and climate finance, said the incentives for cities to deal with climate-change mitigation are very strongly linked to local pollution and economic growth factors. “If you look at China, large city administrations have a very strong incentive to tackle climate-change mitigation because the things you need to do are ones they want to do for other reasons,” he said. “A lot of people are dying from coal pollution, so if you replace coal, you save people from dying and save the planet at the same time.” In addition, cities are often able to wield significant power over local transport, which the United Nations Human Settlements Program says accounts for 23 percent of city greenhouse gas emissions. Thus, city planners can help speed up the implementation of electric vehicles and possibly even self-driving vehicle programs, unlocking “enormous gains in energy efficiency of transport,” Walters said. “It changes things dramatically.” “People talk here when a woman talks to men. They say things like how a woman should not leave the house,” says Runa Jha, a solar entrepreneur in Janakpur, eastern Nepal. “But I don’t care.”
A widow, Jha lives in one room with her three teenage children. In rural Nepal, widows are treated as social outcasts. They are seen as predatory, potential husband-stealers and their interactions with men are frowned upon. “You should do what you want,” says Jha, who received training from Empower Generation – an NGO that on Thursday will be awarded a £20,000 Ashden award for promoting the role of women and girls in the clean energy sector. Another Empower-trained solar entrepreneur, Lalita Choudhary, also faced cultural barriers. “Individuals are going to say all sorts of things” about business women in rural Nepal, she says. Choudhary lives not too far from Jha, in Lahan, Siraha, just 17km from the Indian border. Most people in the area work in agriculture, growing rice and corn or tending to goats and cows. In many communities, women “hide their faces and do not talk to men” and “are not really allowed to get a job,” says Abhilahsa Poudel, Empower Generation’s communications coordinator. But solar power’s effect on village life is inarguable. Its allows for cleaner home environments, with light into the evenings and the ability to charge a mobile phone. The social benefits that flow from the women-run solar businesses, means that Jha and Choudhary have become admired for their work by both men and women in their communities. “Everyone wants to be like [Choudhary] and to work like her,” says Poudel. Jha and Choudhary are two of the 23 women that NGO Empower Generation has trained to be renewable energy entrepreneurs, who in turn, employ and manage a further 170 sales agents. Some of the agents are men, but most are aspirational young women, creating a ripple effect of empowerment through sustainable, profitable employment. “Before, women were not allowed outside the house, and were told not to study as they have to do the housework,” Jha says. Empower Generation mentors and supports women registering their own businesses to sell solar lanterns, solar home systems, clean cook stoves and water filters. The trainee entrepreneurs are given lessons on climate change and the adverse effects of fossil fuels, becoming leaders in their community for promoting renewable energy and environmental awareness. As women do not traditionally work in energy, Empower Generation’s work aims to “really move the needle on how women are valued,” and change the rural Nepalese culture of women being considered to be the property of their husband’s families, says Empower Generation co-founder Anya Cherneff. The “priority is to create badass business women,” says Cherneff. Since owning and running a solar business, Jha has taken on other leadership roles, including leading a community clean-up group. “I feel like I want to lead now; I like to lead,” says Jha. Many of the women working with Empower Generation apply their skills and confidence to further business ventures and other arenas of public life. Choudhary is currently running as a candidate in local government elections, and Sita Adhikari, Empower Generation co-founder is now a United Nations adviser. The Ashden awards ceremony on Thursday will host former US vice-president Al Gore as keynote speaker. Adhikari said that receiving the award “encourages us to work even harder to cultivate more women entrepreneurs who are providing reliable, affordable clean tech solutions.” Australian researchers say they have developed a solar paint that absorbs water vapor and sunlight, generating clean hydrogen energy in a process that offers a potentially limitless source of power. The paint features a new compound that acts like silica gel, a drying agent used in sachets to absorb moisture and keep food fresh. The team from RMIT University in Australia said Wednesday in the journal “ACS Nano” that the new material, synthetic molybdenum-sulfide, also functions as a semiconductor and catalyzes the splitting of water atoms into oxygen and hydrogen. “We found that mixing the compound with titanium oxide particles leads to a sunlight-absorbing paint that produces hydrogen fuel from solar energy and moist air,” lead author Torben Daeneke said. RMIT University is a publicly funded research university in Melbourne. As titanium oxide is a common ingredient in paint, the new material could convert a brick wall into fuel production real estate. “Our new development has a big range of advantages,” Daeneke said. “There’s no need for clean or filtered water to feed the system. Any place that has water vapor in the air, even remote areas far from water, can produce fuel.”
Daeneke’s colleague, Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh, said hydrogen could be used in fuel cells as well as conventional combustion engines. “This system can also be used in very dry but hot climates near oceans,” said Kalantar-zadeh. “The seawater is evaporated by the hot sunlight and the vapor can then be absorbed to produce fuel. This is an extraordinary concept: making fuel from the sun and water vapor in the air. Wind and solar produced 10 percent of the electricity generated in the United States for the first time in March, federal energy officials said Wednesday.
THE HILL — The Energy Information Administration’s (EIA) monthly power report for March found that wind produced 8 percent of the electricity produced in the U.S. that month, with solar producing 2 percent. The two sources combined to have their best month ever in terms of percentage of overall electricity production, EIA said. The agency expects the two sources topped 10 percent again in April but forecasts that their generation will fall below that mark during the summer months. Due to the way geographic wind patterns affect the generation of electricity, the two sources typically combine for their best months in the spring and fall. Annually, wind and solar made up 7 percent of electric generation in 2016, EIA said. EIA’s report comes the day after an annual energy report from BP found renewable energy to be the fastest-growing source of electricity in 2016, growing by 12 percent and producing 4 percent of the world's electricity. Renewable energy advocates have cheered the industry’s growth, calling it a clean, increasingly inexpensive source of electricity. Successful campaign demonstrates commitment many people have for a world powered by solar energy. Powur PBC, an international renewable energy platform, set a world record on May 19, 2017 for the fastest company to raise $1,000,000 in equity crowdfunding after the completion of a recent Series 4 capital raise on according to WeFunder.com, a crowdfunding service that connects startups with investors online. The passing in 2016 of the Regulation Crowdfunding provision of the JOBS Act (Jumpstart Our Business Startups) allowing equity crowdfunding caused an explosion of entrepreneurial companies looking to raise capital from the crowd. The previous record holder, Beta-Bionics, raised $1,000,000 in 64 days. Powur's campaign set the new record in 26 days. Powur CEO Jonathan Budd said: “Solar energy is a growing, unstoppable force still in its early stages. Powur aims to accelerate society’s adoption to solar even faster. The success of this campaign is a clear symbol of the strength of our network and the commitment many people have for a world powered by solar energy.” WeFunder.com Director Dylan Enright said, “Powur smashed previous records on our platform in the first seven days, raising over $550,000. We’re excited to see equity crowdfunding continue to make a difference for companies, and provide opportunity as unaccredited investors realize they can be owners of companies they believe in while still private.”
Powur is a first-of-its-kind platform for renewable energy worldwide. The company has built an international network of Powur Advisors -- home-based solar entrepreneurs who use Powur’s platform to build and operate their own solar sales businesses. Additionally, Powur has developed proprietary technology to enable its Advisors to provide solar systems to their customers through an international network of solar providers. With over 45 solar installers on its platform, Powur covers 29 U.S. states, with recent expansion into Canada, Puerto Rico, and Australia. “This is only the beginning,” Budd said. “We see solar as a multi-trillion-dollar market in the next two decades, and Powur as the category creator for solar and direct selling. We have big goals for this business to reach millions of homeowners and create billions in sales commissions for our Advisors. It’s a lofty vision, but the stakes for our environment have never been higher.” Budd said the company would consider raising an additional crowdfunding round in 2018 to continue to expand its operations worldwide, while creating more valuable products for its ecosystem of customers, advisors, and solar installers. Founded in 2015, California-based Powur PBC is on a mission is to accelerate the adoption of solar energy worldwide. Its proprietary software platform allows its 3,000+ independent contractors to introduce customers to solar via a variety of channels, track customers through the solar cycle, as well as build, monitor and grow their own independent sales organization. For more information, visit https://www.powur.com. |
James Ramos,BPII'm your go to solar energy expert here to guide you step-by-step through all of your solar options. Categories |
James The Solar Energy Expert












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
